Turkey is situated in one of the world’s most active earthquake zones Throughout history, the region has been shaken by numerous powerful earthquakes resulting in massive devastation and loss of life Let’s take a closer look at why Turkey is prone to earthquakes and some of the worst quakes in the country’s history.
Why Turkey Has Frequent Earthquakes
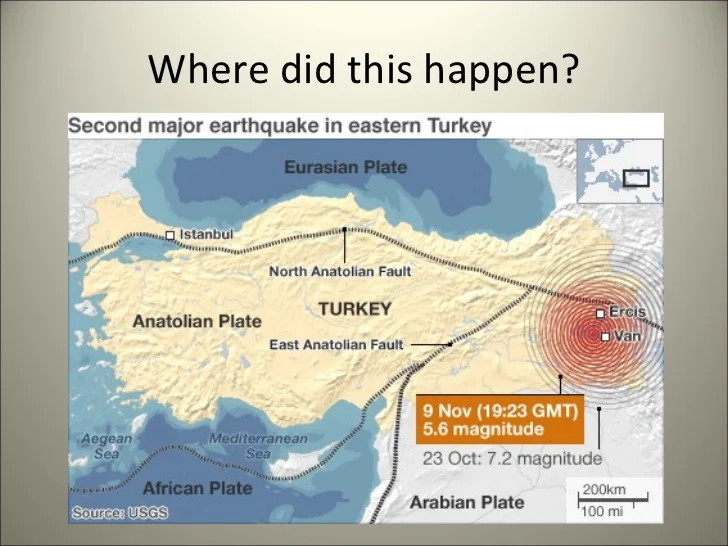
The high frequency of earthquakes in Turkey is due to the country’s location at the boundary between the Anatolian tectonic plate and the Eurasian and African plates. This is an area of intense seismic activity where the plates move and grind against each other, building up pressure that is occasionally released in the form of earthquakes.
Specifically, Turkey lies along:
-
The North Anatolian Fault running across northern Turkey This transform boundary is formed as the Anatolian plate slides westward past the Eurasian plate
-
The East Anatolian Fault running along southeastern Turkey. This is also a transform boundary between the Anatolian and Arabian plates.
-
The Aegean Sea which marks the subduction zone where the African plate is diving under the Anatolian plate, causing frequent seismic activity.
This convergence of three major tectonic plates makes Turkey vulnerable to many types of earthquakes including destructive shallow quakes as well as potentially tsunami-generating megathrust events.
A History of Devastation: Turkey’s Worst Earthquakes
According to records, Turkey has experienced over 100 earthquakes greater than magnitude 6 in the past century alone. Some of the most catastrophic include:
-
The 1509 Istanbul earthquake struck the Sea of Marmara with an estimated magnitude of 7.2, causing a tsunami and killing over 10,000 people.
-
In 1766, an estimated 5,000 people died in the Marmara earthquake near the Dardanelles measuring 7.4 magnitude.
-
The massive Erzincan earthquake in 1939 registered 7.8 magnitude, resulting in 32,700 fatalities.
-
In 1999, the devastating Izmit earthquake struck near Istanbul at 7.6 magnitude, killing over 17,000 people.
-
Most recently in 2023, back-to-back 7.8 and 7.5 magnitude quakes struck southeastern Turkey near Gaziantep province. With over 47,000 fatalities, it ranks as the deadliest natural disaster in modern Turkish history.
Factors Contributing to Earthquake Impact
A variety of factors, both natural and human-caused, influence the destructiveness of earthquakes in Turkey:
-
Proximity to fault lines – Major urban centers like Istanbul and Izmir are located very close to active fault lines, putting millions at risk.
-
Poor construction – Lax enforcement of building codes has led to structures unable to withstand strong shaking. Pancake collapses of multifamily buildings are common.
-
Population density – Turkish cities have grown rapidly, with more people concentrated in vulnerable buildings.
-
Poverty – Poorer rural areas often have the worst damage, with many living in unstable adobe or stone masonry structures.
-
Timing – Nighttime quakes like Erzincan cause more casualties as people are caught unprepared. Cold winter earthquakes also impede rescue efforts.
While Turkey’s location ensures frequent seismic activity is inevitable, improvements in earthquake engineering and preparedness can help mitigate damage and protect human life when the ground starts shaking.
Turkey’s positioning along major fault lines guarantees powerful earthquakes will continue plaguing the country. Over centuries, major quakes have repeatedly brought devastation and mass casualties. The 2023 Turkey-Syria event serves as a reminder that proximity to active tectonic boundaries comes with inherent risks. While earthquakes cannot be prevented, improvements in building safety, emergency response, and public awareness can reduce the impacts of seismic hazards going forward. By understanding the tectonic forces at play and Turkey’s vulnerability, the nation can strive for a more earthquake-resilient future.
Other statistics on the topic

Access all statistics starting from
* For commercial use only
- Free Statistics
Based on your interests
- Free Statistics
- Premium Statistics
- Free + Premium Statistics
- Reports
- Market Insights
Number of earthquakes in Turkey from 1990 to 2023
| Characteristic | Number of earthquakes |
|---|---|
| 2023 | 74,227 |
| 2022 | 20,277 |
| 2021 | 23,763 |
| 2020 | 33,824 |
| 2019 | 23,481 |
| 2018 | 22,899 |
| 2017 | 38,287 |
| 2016 | 20,541 |
| 2015 | 22,290 |
| 2014 | 24,132 |
| 2013 | 23,607 |
| 2012 | 26,973 |
| 2011 | 29,831 |
| 2010 | 19,023 |
| 2009 | 15,211 |
| 2008 | 11,754 |
| 2007 | 7,820 |
| 2006 | 5,038 |
| 2005 | 9,481 |
| 2004 | 7,682 |
| 2003 | 1,914 |
| 2002 | 1,078 |
| 2001 | 599 |
| 2000 | 745 |
| 1999 | 2,101 |
| 1998 | 643 |
| 1996 | 169 |
| 1995 | 447 |
| 1994 | 304 |
| 1992 | 507 |
| 1991 | 380 |
| 1990 | 344 |
1990 to 2023 Supplementary notes
Release date is the day of access.Citation formats
Why do earthquakes keep happening in Turkey and Syria? | Al Jazeera Newsfeed
FAQ
Are earthquakes common in Turkey?
Is Turkey risky for earthquake?
When was Turkey’s last earthquake?
|
Date
|
Region
|
Magnitude
|
|
02/06/2023
|
Turkey; Syria
|
7.5
|
|
02/06/2023
|
Kahramanmaras; Syria
|
7.8
|
|
10/30/2020
|
Samos; Turkey (Izmir)
|
7.0
|
|
06/25/2020
|
Van
|
5.4
|
How likely is Turkey to have another earthquake?
