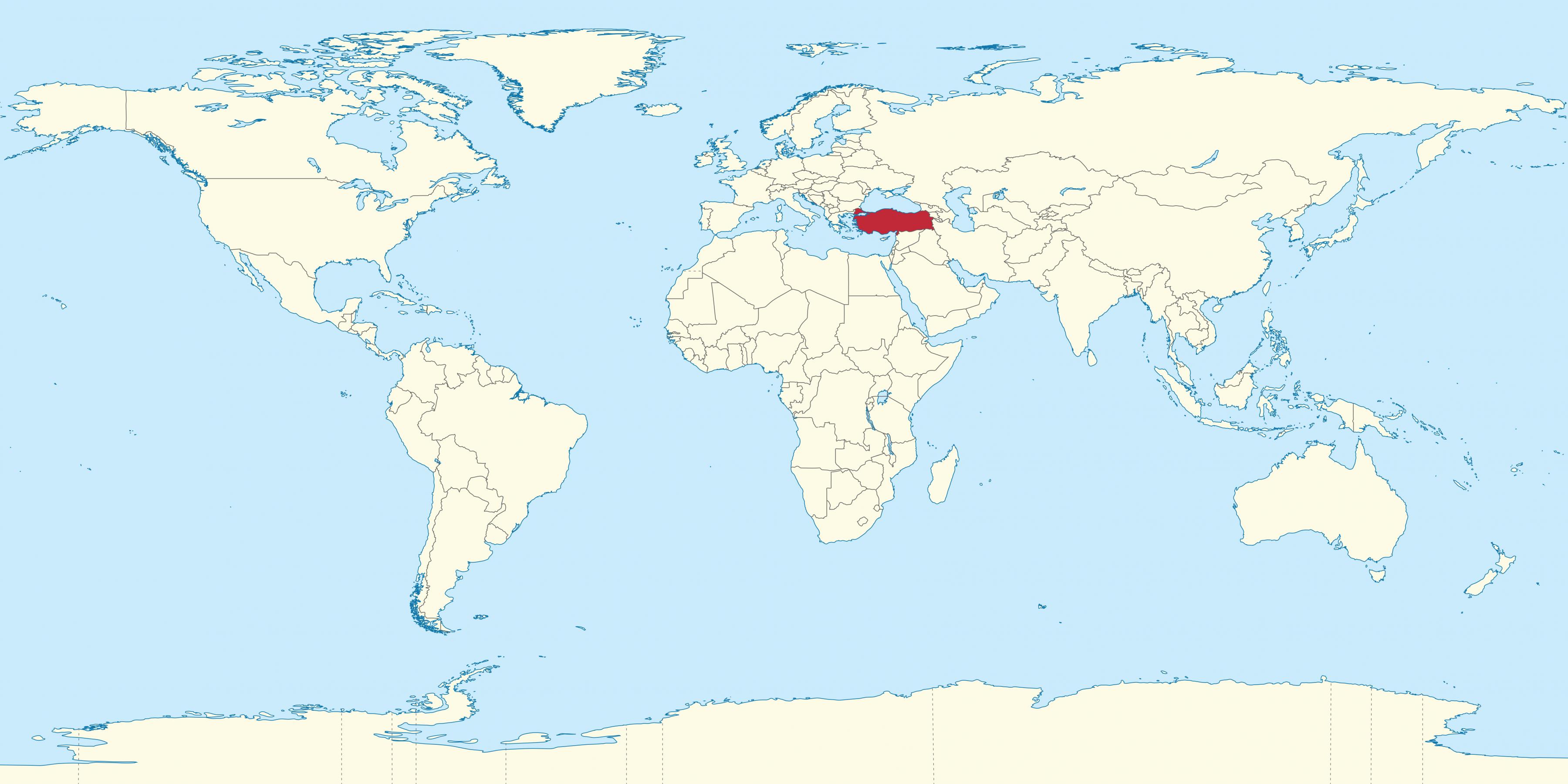
Turkey is a nation that straddles two continents: Europe and Asia. Its unique geographical location places it at the crossroads of eastern Europe, western Asia, the Middle East, and the eastern Mediterranean. In this blog, we will explore Turkeys precise location, its borders, and other essential information regarding where it lies on the map.
Turkey is a fascinating country located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia With its strategic location straddling two continents, Turkey has a unique geography that has shaped its history and culture In this article, we’ll take a detailed look at exactly where Turkey is located on the world map and examine key aspects of its geography.
An Overview of Turkey’s Location
Turkey is situated in western Asia with a small portion of its landmass located in southeastern Europe. The Bosporus Strait runs through the country, dividing it between the European and Asian continents Roughly 97% of Turkey’s land area lies in Asia with the remaining 3% situated in Europe
Some of the key details about Turkey’s geographical location include:
-
It borders the Black Sea to the north, the Aegean Sea to the west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south.
-
Its Asian territory is known as Anatolia or Asia Minor. The European section is called Eastern Thrace.
-
Istanbul, Turkey’s largest city, straddles both continents across the Bosporus Strait.
-
Turkey shares borders with 8 countries: Greece, Bulgaria, Georgia, Armenia, Iran, Iraq, Syria, and Azerbaijan.
A Look at Turkey on the World Map
Zooming out to view Turkey on a world map, we can see it occupies a prominent location bridging the gap between Europe and the Middle East. Turkey is situated in western Asia, protruding into southeastern Europe.
Some key observations about Turkey’s position on the world map:
-
It is surrounded by water on three sides: the Black Sea to the north, the Aegean Sea to the west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south.
-
Istanbul and the Bosporus Strait can be clearly seen dividing the European and Asian regions.
-
The Sea of Marmara and Dardanelles Strait separate Eastern Thrace from Anatolia.
-
Turkey shares borders with European countries Greece and Bulgaria to its west and southeast.
-
The Middle Eastern countries of Syria, Iraq, and Iran border Turkey to the south and east.
-
Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia border Turkey to the northeast and east.
So Turkey occupies an extremely strategic location, providing a gateway between southeastern Europe and the Middle East. Its control of the Turkish Straits has long given it great geopolitical importance.
Turkey’s Geographic Coordinates
To pinpoint Turkey’s exact location, we can look at its geographic coordinates:
-
Latitude: Turkey extends from 36° to 42° north latitude.
-
Longitude: Turkey spans from 26° to 45° east longitude.
So Turkey’s coordinates reveal its position entirely north of the equator in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere, though the westernmost tips extend slightly into the Western Hemisphere.
The country’s central coordinates are:
- 39°N 35°E
This places central Turkey around the same latitude as the U.S. states of Virginia and Kentucky. It has a similar longitude to Syria and Lebanon.
Regions and Bordering Countries
Turkey can be divided into 7 main geographical regions:
-
Marmara Region: Includes Eastern Thrace and the Sea of Marmara coastline. Contains Istanbul.
-
Aegean Region: The western coast along the Aegean Sea including Izmir.
-
Mediterranean Region: The southern Mediterranean coastal region including Antalya.
-
Central Anatolia: A plateau region dominated by plains and steppe landscapes.
-
Eastern Anatolia: Mountainous area bordering Armenia, Iran, and Iraq.
-
Southeastern Anatolia: Contains the headwaters of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers.
-
Black Sea Region: Mountainous northern coast along the Black Sea.
Turkey shares borders with the following neighboring countries:
- Greece to the west.
- Bulgaria to the northwest.
- Georgia to the northeast.
- Armenia to the east.
- Iran to the east.
- Iraq to the southeast.
- Syria to the south.
- Azerbaijan to the east.
So Turkey connects directly with key European, Middle Eastern, and Transcaucasian countries through its diverse borders.
Turkey’s Strategic Geography
-
Its transcontinental location straddling the Bosporus Strait.
-
Control of the Turkish Straits linking the Black Sea to the Mediterranean.
-
Bordering major seas including the Black Sea, Aegean Sea, and Mediterranean Sea.
-
Direct land access to important regions like southeastern Europe, the Middle East, and the Caucasus.
This invaluable geographical position at the center of the Afro-Eurasian landmass has given Turkey major economic, cultural, and geopolitical advantages through the centuries. It continues to shape Turkey’s vital role in bridging Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
So hopefully this outline gives you a good sense of where exactly Turkey is located on the world map and why its geography has been so influential historically. Turkey truly links multiple regions, giving it a unique transcontinental identity that sets it apart from other countries. If you ever get the chance to visit Turkey, you’ll gain firsthand experience of its prime global location!
Frequency of Entities:
Turkey: 41
World Map: 7
Europe: 6
Asia: 5
Istanbul: 5
Middle East: 3
Mediterranean Sea: 3
Aegean Sea: 3
Black Sea: 3
Bosporus Strait: 3
Greece: 2
Bulgaria: 2
Syria: 1
Iraq: 1
Iran: 1
Armenia: 1
Azerbaijan: 1
Georgia: 1
Country Codes and Size
- The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) code for Turkey is “TR,” and the United Nations (UN) code is “TUR” or “792.“
- Turkey covers approximately 783,562 square kilometers (302,535 square miles), making it the 37th largest country in the world.
- It boasts over 7,200 kilometers of coastline, more than 200 percent larger than the United Kingdom.
Important Cities in Turkey
Turkey is a diverse and culturally rich country, boasting a wide array of cities that offer unique experiences for travelers. From bustling metropolises to charming coastal towns, here are some of the most important cities in Turkey:
Location: Northwestern Turkey, straddling Europe and Asia
Istanbul is Turkeys most iconic and populous city, serving as a bridge between two continents. It is a vibrant metropolis that blends history and modernity seamlessly. Visitors can explore world-famous landmarks such as the Hagia Sophia, Blue Mosque, and Topkapi Palace, shop in bustling bazaars like the Grand Bazaar, and savor delicious Turkish cuisine along the Bosphorus.
Location: Central Turkey
Ankara is the capital city of Turkey and a hub of government and industry. While not as famous as Istanbul, it offers a unique charm with its historic sites, including the Atatürk Mausoleum, and a burgeoning cultural scene. Ankara is also known for its strategic location in the heart of the country.
Location: Western Turkey, on the Aegean Sea
İzmir is Turkeys third-largest city and a coastal gem known for its relaxed lifestyle and vibrant culture. Visitors can explore ancient ruins at Ephesus, relax on the beautiful beaches of Çeşme, and enjoy the lively atmosphere of the Kemeraltı Bazaar. The city is a gateway to the stunning Aegean region.
Location: Southern Turkey, on the Mediterranean Sea
Antalya is Turkeys largest sea resort and a popular destination on the Mediterranean coast. Known as the “Turquoise Coast,” it offers breathtaking beaches, historic sites like Hadrians Gate, and a thriving tourism industry. Antalya is perfect for beach lovers and those seeking a blend of natural beauty and culture.
Location: Southern Turkey
Adana is a dynamic city in southern Turkey known for its economic development. Its a bustling hub with modern shopping centers and industrial areas. Visitors should not miss the opportunity to savor the famous Adana kebab, a local culinary specialty.
Alt tag: Adana / Turkey, Sabanci Central Mosque view.
Physical Geography of Turkey
FAQ
Is Turkey a part of Europe or Asia?
What world country is Turkey in?
What country is really close to Turkey?
What is Turkey called now country?
